peach tree borer life cycle
The adult female lays eggs in bark crevices. Females each lay between 80 and 90 eggs on fruit shoots or the undersides of leaves next to veins.

Peachtree Borer Nectarine Agriculture Pest Management Guidelines Uc Statewide Ipm Program Uc Ipm
Peach tree borers overwinter as partially grown larvae in a gallery under the bark.
. Larvae eat an exit hole nearly through the bark spin a cocoon and pupate in a small cavity. Look for injury symptoms when pruning trees in the spring and early summer. Larvae become active and resume feeding in April with larger larvae.
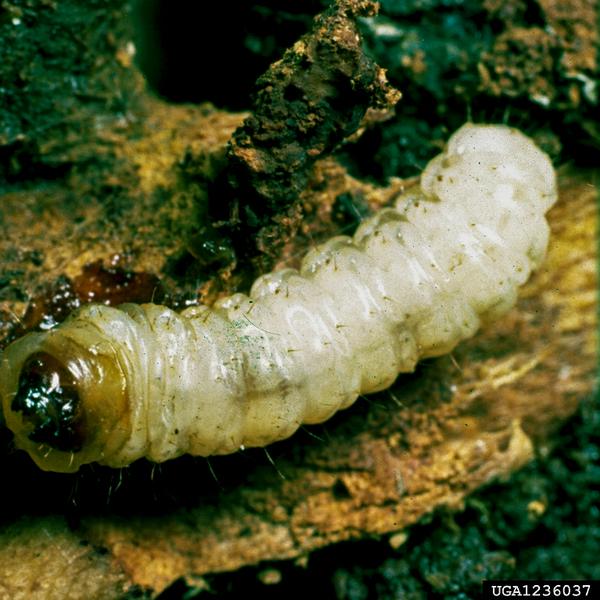
The light intersegmental membranes contrasted with the brown body distinguishes peach twig borer from other larvae found in stone fruits. Larvae hatch in 8 to 9 days and bore into the main trunk and larger roots near the soil surface. Borers overwinter as larvae in the tunnels and resume feeding the following spring.
In the spring feeding is resumed and the larval period is completed. The adult borer emerges in the late spring and early summer. Hatching larvae tunnel into the tree at or slightly below ground level.
Hatching larvae tunnel into the tree at or slightly below ground level. Adults which resemble wasps are most prevalent from mid-May to early October. The period of time required to complete a life cycle varies considerably throughout the range of the peachtree borer.
Small larvae of peach twig borer are almost white with a distinct black head. Borer damage is usually attended by gumming with varying amounts of frass in the gum. This borer overwinters in a wide range of larval stages.
Damage Any wound on stone fruit trees may cause gum to exude. Upon hatching from the eggs Figure 4. This is in contrast to lesser peachtree borer which may feed on any part of the tree Root feeding leads to reduced crop bearing capacity due to lack of nutrient uptake while heavy trunk feeding can.
If a plant is healthy the larvae may be killed by sap flow. The lesser peachtree borer overwinters as larvae and reaches full growth during April and May. Life cycles of peachtree borers and lesser peachtree borers.
Peach twig borer has about 30 known species of natural enemies. Adult beetles are dark metallic brown to dull gray about 12 inch long. The borer has a two-year life cycle.
Bark of the lower trunk or in the soil near the trunk base or by a larva andor larval tunnel under the bark Fig. Upon hatching the larvae bore just beneath the bark near the ground level and into the roots to feed on growing tissue and inner bark. The larvae can develop equally well in shoots or immature fruit.
Seasonal development and life cyclePeachtree borer. Another commonly found parasite is Macrocentrus ancylivorus which attacks both peach twig borer and Oriental fruit moth. As larvae mature they become chocolate brown with alternating dark and light bands around the abdomen.
It is reported that it takes two years to complete a life cycle in Canada and in a small percentage of populations in New York. Mature larvae are about 0. In some years and orchards these natural.
Most individuals complete development during the summer. Life Cycle Appearance. Adult moths of the lesser peachtree borer emerge from late May through September while peachtree borers emerge from midJune to early September.
Only the immature larva stage Figure 3 produces the damage to trees. The peach tree borer is an insect pest that attacks peaches Prunus persica as well all other members of the Prunus genus including cherries plums nectarines and apricots. The lesser borer completes about one and one-half cycles a year.
Only the immature larva stage Figure 3 produces the damage to trees. The adult peachtree borer is a steel blue to black moth that resembles a wasp. The clear-winged female moths lay their eggs on the bark at the base of tree trunks in mid- to late-summer.
The newly hatched larvae bore into the inner bark forming tunnels and filling them with frass. The eggs which are laid singly hatch in 5 to 18 days depending on temperature. Among those commonly found in California are the chalcid wasps Copidosoma Paralitomastix varicornis and Euderus Hyperteles lividus.
Life Cycle and Damage. Adult peachtree borers emerge in the late spring or early summer. Peachtree borer has a single generation per year but it can result in severe losses if not managed correctly.
Produced by peachtree borer. The first summer generation larvae develop during late May and June. The presence of small particles of wood and bark within the gum distinguish damage by peachtree borer Life History and Habits The life cycle of the peachtree borer requires one year to complete.
Eggs typically are inserted into the bark of the trunk near the ground although eggs may occasionally be laid in tree crotches. The peach tree borer completes one life cycle a year. Adult beetles usually appear in May and June with egg-laying continuing until late July.
Because the egg laying period is so long overwintering larvae vary greatly in size. When mature the larva constructs a cocoon under the bark at or near soil level and pupates. Lesser peachtree borer infestations are almost always associated with areas on the.
Upon hatching from the eggs Figure 4 y. They feed on cambium tissue and eventualy weaken or kill the tree. The larval stage of PTB is an indirect pest of stone fruit trees.
Larvae tunnel primarily into the lower trunk and roots feeding on growing tissue and inner bark. Female Peachtree Borers lay their eggs on the tree trunks or at the base of the tree and lay 500-600 eggs on average. Winter is spent as a larva under the bark in the cambium layer.
The life cycle of the peachtree borer requires one year to complete. Evidence of peach borer damage can usually be seen in spring and summer with affected trees quickly declining in health. Female moths lay their eggs during the summer on bark at the base of tree trunks.
The peachtree borer overwinters as a partly grown larva in its burrow beneath the bark of the tree. Egg laying begins soon after emergence and mating and larvae tunnel into the bark to feed until the. During this time eggs are laid on the trunks of trees hatching within a week to ten days.
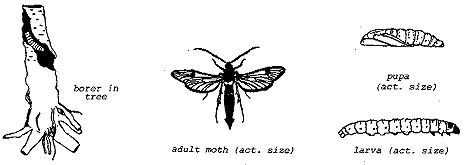
Peachtree borer life cycle showing larva 1 cocoon 2 empty pupal case 3 and cocoon with pupa emerging 43. In 3 to 4 weeks a clearwinged moth emerges leaving an empty pupal skin projecting from the burrow. Usually they are close to or below ground level.

Peachtree Borer Oklahoma State University
Pests Bc Tree Fruit Production Guide
Lords Environmental Peach Tree Borers

Peach Tree Borer Fairfax Gardening

Peach Tree Borers How To Control Peach Tree Borers

Peachtree Borer Nc State Extension Publications

Peachtree Borer Nc State Extension Publications
Pests Bc Tree Fruit Production Guide
Peachtree Borer Wsu Tree Fruit Washington State University
Pests Bc Tree Fruit Production Guide

Peach Tree Borer Trap Pest Control From Gardens Alive

Lesser Peachtree Borer Damage Stock Image C025 7085 Science Photo Library
Eny 691 In489 Peachtree Borers In The Home And Commercial Peach Orchard

Peach Tree Borer Treatment Control Planet Natural
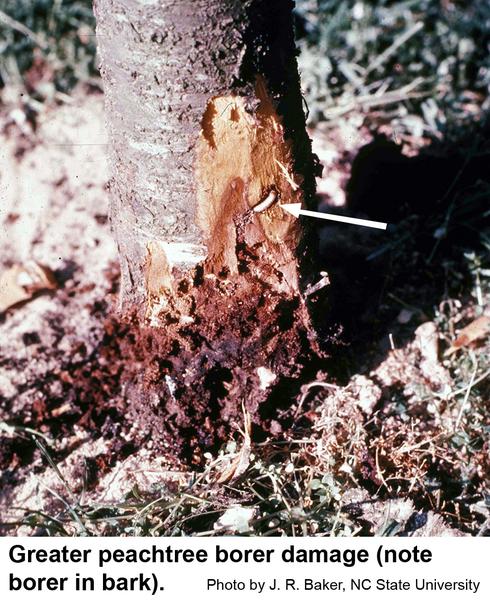

Greater Peachtree Borer In The Landscape Nc State Extension Publications



